2.3-The Peninsular Plateau
2.3-The Peninsular Plateau Important Formulae
You are currently studying
Grade 9 → Geography → Physical Features of India → 2.3-The Peninsular Plateau
2.3 - The Peninsular Plateau
- The Peninsular Plateau is a large, elevated region in India.
- It is made up of old crystalline rocks, mainly granite and gneiss.
- It is divided into two main regions: the Central Highlands and the Deccan Plateau.
- The Plateau has a gently sloping surface and is rich in minerals.
- Rivers like the Narmada, Tapi, and Mahi flow through it, creating deep valleys.
- The highest point is the Anaimudi Peak in Kerala (2,695 m above sea level).
- The region is important for agriculture, mining, and biodiversity.
2.3 - The Peninsular Plateau
The Peninsular Plateau is a prominent geographical feature of India, covering a large part of the southern and central regions of the country. Characterized by its elevated terrain, this plateau is significant for its geological formations, climate, and economic importance.
Geographical Extent
The Peninsular Plateau is bounded by several important geographical features:
- Location: It is situated to the south of the Northern Plains and extends from the Vindhya Range in the north to the southernmost tip of India.
- Boundaries: The plateau is bordered by the Western Ghats to the west and the Eastern Ghats to the east, forming a triangular shape.
- Area: It covers an extensive area of approximately 1.6 million square kilometers, comprising various states, including Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
Geological Features
The Peninsular Plateau is characterized by ancient crystalline rocks, making it one of the oldest landforms in India:
- Rock Types: It mainly consists of igneous and metamorphic rocks, including granite, gneiss, and basalt.
- Rivers: Major rivers such as the Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri originate from this plateau, flowing towards the east coast of India.
- Landforms: The region features several plateaus, hills, and valleys, with notable hill ranges like the Vindhyas and Satpuras.
Climate
The climate of the Peninsular Plateau varies due to its elevation and geographical location:
- Seasons: The region experiences three main seasons: summer, monsoon, and winter.
- Temperature: Summer temperatures can rise above 40°C, while winters are relatively mild, especially in the southern parts.
- Rainfall: The monsoon season brings significant rainfall, primarily from the southwest monsoon, which is crucial for agriculture.
Flora and Fauna
The Peninsular Plateau supports diverse flora and fauna:
- Vegetation: The region is characterized by mixed deciduous forests, grasslands, and scrub vegetation, which provide habitats for various species.
- Wildlife: Protected areas like Bandipur National Park and Nagarhole National Park are home to species such as elephants, tigers, and leopards.
- Agricultural Practices: The fertile soil in certain areas supports the cultivation of crops such as rice, pulses, and millets.
Economic Significance
The Peninsular Plateau is vital to India's economy:
- Agriculture: The region is known for its agricultural output, particularly in crops like cotton, groundnuts, and sorghum.
- Mineral Resources: Rich in minerals, the plateau is a significant source of coal, iron ore, manganese, and bauxite, contributing to industrial development.
- Industrial Growth: Major cities like Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Pune have developed into important industrial and technological hubs.
Challenges
The Peninsular Plateau faces several challenges that impact its environment and economy:
- Drought: Certain regions experience drought due to irregular rainfall patterns, affecting agricultural productivity.
- Deforestation: Increasing urbanization and agricultural expansion lead to deforestation, threatening biodiversity.
- Soil Erosion: Erosion due to deforestation and improper land use practices poses a risk to soil fertility.
Cultural Aspects
The Peninsular Plateau is rich in cultural heritage:
- Historical Sites: The region is home to ancient temples, forts, and monuments, reflecting its historical significance.
- Tribal Communities: Various tribal communities inhabit the plateau, preserving unique traditions and lifestyles.
- Festivals and Arts: The area celebrates vibrant festivals and showcases traditional art forms, contributing to India's cultural diversity.
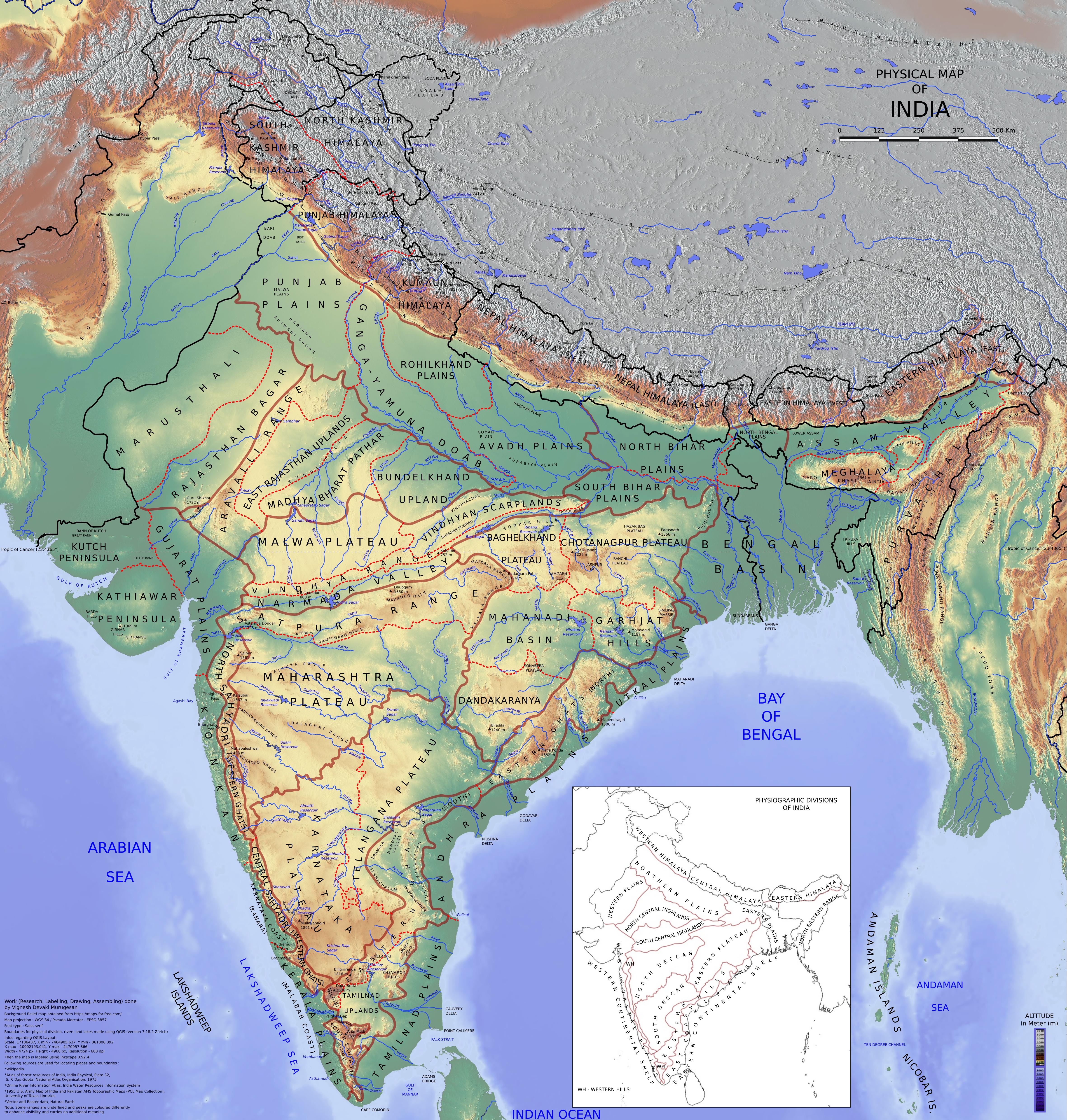
Vigneshdm1990, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
2.3- The Peninsular Plateau
भारत का उपमहाद्वीप एक प्राचीन प्लेटो (उच्च स्थल) है, जिसे "पेनिन्सुलर प्लेटो" (Peninsular Plateau) कहा जाता है। यह क्षेत्र देश के दक्षिणी भाग में स्थित है और यह एक बड़ी भूमि का हिस्सा है। यह क्षेत्र पर्वत श्रृंखलाओं, घाटियों, पठारों और नदी प्रणालियों से घिरा हुआ है। पेनिन्सुलर प्लेटो भारत के लगभग तीन-चौथाई क्षेत्र को कवर करता है।
विशेषताएँ
पेनिन्सुलर प्लेटो का भूगोल बहुत विविध है और इसमें कई महत्वपूर्ण विशेषताएँ हैं:
- उचाई: यह क्षेत्र समुद्रतट से 600-900 मीटर की ऊंचाई पर स्थित है। हालांकि, कुछ स्थानों पर यह ऊचाई 1000 मीटर तक पहुँच जाती है।
- समतल और ढलान: अधिकांश भाग समतल है, लेकिन कुछ हिस्सों में यह उबड़-खाबड़ और पहाड़ी है। यह मुख्य रूप से क्रिस्टलीय शिलाओं से बना है, जैसे कि गनीस, बेसाल्ट और शैल (Shale)।
- प्राचीन शिलाएँ: पेनिन्सुलर प्लेटो का अधिकांश हिस्सा प्राचीन शिलाओं का बना हुआ है, जिन्हें "वयस्क शिलाएँ" (Archaean Rocks) कहा जाता है।
- नदियाँ और जलवायु: इस क्षेत्र में बहने वाली प्रमुख नदियाँ, जैसे कि गोदावरी, कृष्णा, कावेरी और नर्मदा, मुख्य जल स्रोत हैं। यहाँ की जलवायु अधिकांशतः गर्म और शुष्क होती है।
उपखंड
पेनिन्सुलर प्लेटो को विभिन्न उपखंडों में विभाजित किया जा सकता है:
- मालवा पठार: यह मध्यभारत में स्थित है और इसकी उचाई 450-600 मीटर के बीच होती है।
- देक्कन पठार: यह भारत के दक्षिणी हिस्से में स्थित है और इसकी उचाई 600-900 मीटर के बीच होती है। यह मुख्य रूप से बेसाल्ट शिलाओं से बना हुआ है।
- कर्नाटक पठार: यह कर्नाटक और आंध्र प्रदेश के क्षेत्रों में फैला हुआ है। यह क्षेत्र उच्च उचाई वाले क्षेत्रों और घाटियों से घिरा हुआ है।
नदियाँ और जलप्रवाह
पेनिन्सुलर प्लेटो के प्रमुख जलप्रवाह नीचे दिए गए हैं:
- नर्मदा नदी: यह नदी मध्यप्रदेश से निकलती है और अरब सागर में गिरती है। यह भारत की एकमात्र नदी है जो पश्चिम की ओर बहती है।
- गोदावरी, कृष्णा, और कावेरी नदियाँ: ये नदियाँ दक्षिण भारत में बहती हैं और इनका जलवहन बहुत महत्वपूर्ण है।
आकृति और भूविज्ञान
पेनिन्सुलर प्लेटो एक प्राचीन भूमि है, जिसे अरब सागर, बंगाल की खाड़ी और भारतीय महासागर से घेर लिया गया है। इस प्लेटो का गठन बहुत पहले हुआ था, जब यह एक स्थिर भूमि के रूप में उभरा।
भूतकालिक प्रक्रियाएँ
पेनिन्सुलर प्लेटो का भूगर्भीय गठन कई प्रकार की प्रक्रियाओं का परिणाम है। इन प्रक्रियाओं में ज्वालामुखी गतिविधियाँ, नदियों द्वारा कटाव और पहाड़ों के बनते हुए स्थलाकृतिक रूप शामिल हैं।
महत्वपूर्ण पहाड़ियाँ और पर्वत
पेनिन्सुलर प्लेटो में कुछ प्रमुख पर्वत श्रृंखलाएँ भी हैं:
- सतपुड़ा पर्वत: यह मध्यभारत में स्थित है और यह नर्मदा नदी के उत्तर में स्थित है।
- विंध्याचल पर्वत: यह उत्तर और दक्षिण भारत को विभाजित करने वाली पर्वत श्रृंखला है।
- अरेबिल पर्वत: यह दक्षिण भारत के पूर्वी किनारे पर स्थित है।
संबंधित गणितीय रूप
पेनिन्सुलर प्लेटो का आकार और इसकी भूगोलिक स्थिति इस प्रकार व्यक्त की जा सकती है:
$$ A = \pi r^2 $$जहाँ A क्षेत्रफल है और r उस क्षेत्र का त्रिज्या है।
इस तरह से पेनिन्सुलर प्लेटो का भूगोल और पर्यावरणीय स्थिति भिन्न-भिन्न क्षेत्रीय विशेषताओं के आधार पर विविध रूप में देखा जा सकता है।
