4.4-What is Globalisation
4.4-What is Globalisation Important Formulae
You are currently studying
Grade 10 → Economics → Globalisation and the Indian Economy → 4.4-What is Globalisation
- Explain the working of the Global Economic phenomenon.
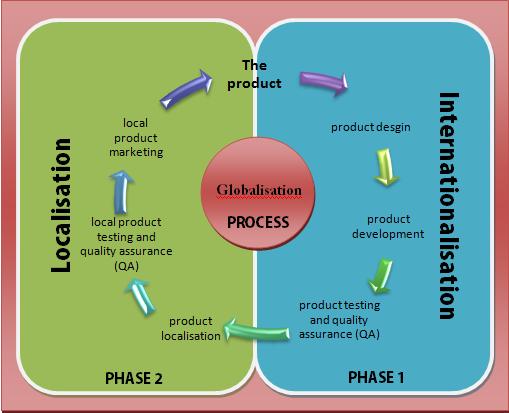
4.4 - What is Globalisation
- Globalisation refers to the increasing interconnection of the world through trade, communication, and technology.
- It involves the integration of economies, societies, and cultures worldwide.
- Key factors include advancements in transport, communication, and the internet.
- Multinational corporations play a significant role in globalisation.
- Globalisation promotes international trade and investment flows.
- The concept leads to the spread of ideas, technologies, and cultures across borders.
- It impacts employment, economic growth, and income distribution.
- Globalisation can create both opportunities and challenges for countries.
Globalisation is a multifaceted phenomenon that has transformed the way countries interact economically, socially, and culturally. Understanding globalisation is essential for grasping its impact on the world economy and individual nations, including India.
Definition of Globalisation: Globalisation refers to the process through which economies, societies, and cultures become interconnected and interdependent on a global scale. This interconnectedness is facilitated by advancements in technology, communication, and trade.
Key Aspects of Globalisation: Globalisation encompasses various dimensions that contribute to its overall impact:
- Economic Globalisation: This aspect involves the integration of national economies through trade, investment, and capital flows. It includes the establishment of multinational corporations that operate across borders and engage in international trade.
- Cultural Globalisation: Cultural globalisation refers to the spread of ideas, values, and cultural practices across the globe. This can lead to a blending of cultures, influencing lifestyle, consumer behavior, and social norms.
- Political Globalisation: Political globalisation involves the increasing influence of international organizations and agreements, which can shape national policies and regulations. Entities like the United Nations, World Trade Organization, and International Monetary Fund play crucial roles in this context.
- Technological Globalisation: Advancements in technology, particularly in communication and transportation, have facilitated faster and easier connections between people and businesses across the world.
Drivers of Globalisation: Several factors contribute to the acceleration of globalisation:
- Trade Liberalization: The reduction of tariffs and trade barriers encourages the free flow of goods and services between countries, promoting global trade.
- Advancements in Technology: Innovations in communication technologies, such as the internet and mobile communication, have made it easier for businesses to operate internationally.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Increased FDI allows companies to establish operations in different countries, fostering economic links and facilitating global business operations.
- Global Supply Chains: Companies often source materials and components from various countries, creating interconnected production networks that span the globe.
Impact of Globalisation on Economies: Globalisation has profound effects on national economies, including:
- Economic Growth: Countries that embrace globalisation often experience economic growth as they gain access to larger markets and increased investment opportunities.
- Job Creation: Globalisation can lead to job creation in sectors that expand due to increased trade and investment, although it may also result in job losses in industries that cannot compete with foreign firms.
- Consumer Choices: Globalisation increases the variety of goods and services available to consumers, enhancing their choices and lowering prices due to increased competition.
- Technology Transfer: Globalisation facilitates the transfer of technology and innovation between countries, promoting development and efficiency in production processes.
Challenges of Globalisation: While globalisation presents numerous opportunities, it also poses significant challenges:
- Income Inequality: Globalisation can exacerbate income inequality both within and between countries, as certain sectors and regions may benefit more than others.
- Cultural Erosion: The spread of global culture can threaten local cultures and traditions, leading to a loss of cultural identity.
- Environmental Concerns: Increased production and consumption can lead to environmental degradation, as countries may prioritize economic growth over sustainable practices.
- Vulnerability to Global Shocks: Countries that are heavily integrated into the global economy may be more susceptible to economic downturns, pandemics, or geopolitical tensions.
Globalisation in the Indian Context: In India, globalisation has significantly influenced economic policies and growth since the 1991 economic reforms. The country has embraced global trade, attracted foreign investment, and experienced rapid economic growth. However, it also faces challenges such as income disparity and the need for sustainable development.
Understanding globalisation is essential for navigating the complexities of the modern world, as it continues to shape economies and societies globally.
4.4 - What is Globalisation
वैश्वीकरण (Globalisation) एक प्रक्रिया है, जिसके तहत देशों के बीच आर्थिक, सांस्कृतिक और सामाजिक संबंध बढ़ते हैं। इसमें व्यापार, निवेश, सूचना, और तकनीकी प्रगति के माध्यम से देशों का एक-दूसरे से जुड़ना शामिल होता है। वैश्वीकरण का उद्देश्य बाजारों और आर्थिक अवसरों को वैश्विक स्तर पर एकीकृत करना है। इस प्रक्रिया ने पूरी दुनिया को एक वैश्विक गांव की तरह बना दिया है।
वैश्वीकरण की शुरुआत 20वीं सदी के अंत में हुई, जब दुनिया में सूचना और संचार प्रौद्योगिकी में तेजी से बदलाव आया। इंटरनेट और अन्य तकनीकी नवाचारों ने दुनिया को एक दूसरे से जोड़ने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाई। इसके कारण कंपनियाँ और सरकारें अपने उत्पादों और सेवाओं को दुनिया भर में वितरित करने में सक्षम हो गईं।
वैश्वीकरण में दो मुख्य पहलू होते हैं:
- आर्थिक वैश्वीकरण: यह व्यापार, निवेश, पूंजी प्रवाह, और वैश्विक आपूर्ति श्रृंखलाओं के रूप में होता है। कंपनियाँ एक दूसरे देशों में उत्पादन करती हैं और सामान व सेवाओं का आदान-प्रदान करती हैं।
- सांस्कृतिक वैश्वीकरण: इसमें विभिन्न संस्कृतियों का आपस में मिलना और विचारों, भाषाओं, और जीवनशैली का आदान-प्रदान शामिल है। यह फिल्म, संगीत, फैशन और खानपान के माध्यम से होता है।
वैश्वीकरण का प्रभाव भारत की अर्थव्यवस्था पर बहुत गहरा पड़ा है। भारत ने 1991 में आर्थिक सुधारों की शुरुआत की, जिसके बाद वैश्विक बाजारों के साथ इसका संबंध बढ़ा। इन सुधारों ने भारत को बाहरी निवेश आकर्षित करने और अपनी वस्तुओं का निर्यात बढ़ाने में मदद की।
वैश्वीकरण से पहले भारतीय अर्थव्यवस्था ज्यादातर घरेलू उत्पादन और व्यापार पर निर्भर थी, लेकिन अब विदेशी कंपनियाँ भारत में निवेश कर रही हैं और भारतीय उत्पादों की मांग दुनिया भर में बढ़ी है। इस प्रकार, वैश्वीकरण ने भारत के आर्थिक विकास में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाई है।
वैश्वीकरण के कई लाभ और नुकसान हैं:
- लाभ:
- वैश्विक बाजारों में भारत की उपस्थिति बढ़ी है।
- भारत में रोजगार के अवसरों में वृद्धि हुई है।
- नई तकनीक और प्रौद्योगिकियों का भारत में आगमन हुआ।
- नुकसान:
- छोटे और घरेलू उद्योगों पर दबाव पड़ा है।
- समाजिक असमानता बढ़ी है, क्योंकि संपन्न और गरीब वर्गों के बीच अंतर बढ़ गया है।
- संस्कृतिक परिवर्तन भी देखा गया है, जिससे पारंपरिक सांस्कृतिक पहचान पर असर पड़ा है।
वैश्वीकरण का एक और महत्वपूर्ण पहलू यह है कि यह अंतर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार के नियमों और संस्थाओं जैसे विश्व व्यापार संगठन (WTO) द्वारा नियंत्रित होता है। ये संगठन वैश्विक व्यापार को समन्वित करते हैं और देशों के बीच व्यापार विवादों को हल करने में मदद करते हैं।
वैश्वीकरण के प्रभावों को समझने के लिए अर्थशास्त्रियों ने कुछ गणनाएँ और मॉडल भी विकसित किए हैं। जैसे, व्यापार को बढ़ावा देने के लिए निम्नलिखित सूत्र का उपयोग किया जाता है:
$E = P + Q + I + T$
जहां, E = कुल आर्थिक गतिविधि, P = उत्पादन, Q = गुणवत्ता, I = निवेश, और T = व्यापार हैं। यह सूत्र देशों के बीच आपसी व्यापार और उत्पादन को जोड़ने में मदद करता है।